Sách trắng CENTUS
Giới thiệu
Nhiều loại tiền kỹ thuật số đã được tạo ra trong thế giới hiện đại và đang được sử dụng như một loại tiền gần như. Tiền điện tử thường có các chức năng tương tự như tiền được phát hành ở cấp độ quy định của nhà nước và hoạt động như một công cụ trung gian trong trao đổi hàng hóa.
Cũng giống như tiền do nhà nước phát hành (fiat), tiền kỹ thuật số trải qua một giai đoạn phát triển liên tục đầy đủ cùng với quá trình phát triển vô tận của xã hội:
– Đáp ứng nhanh tiến bộ khoa học và công nghệ. Tất cả các thành tựu kỹ thuật và công nghệ được thực hiện trong quá trình sản xuất tiền.
– Tăng tốc độ lưu thông tiền, và kết quả là tốc độ thanh toán. Đổi lại, xu hướng này bị hạn chế trong sự tăng trưởng của giá tăng tốc thanh toán (sự tăng trưởng của hoa hồng để thực hiện và các chi phí khác) và bảo mật của nó (tham vọng giảm thiểu rủi ro mất tiền trong quá trình thanh toán).
– Tăng tính sẵn có của các công cụ thanh toán và khả năng kiểm soát quá trình chuyển tiền. Các doanh nghiệp và người mua cố gắng sử dụng các công cụ thanh toán đơn giản và giá cả phải chăng nhất.
Tuy nhiên, với tất cả những lợi thế rõ ràng của việc sử dụng tiền kỹ thuật số trong hệ thống thanh toán, tiết kiệm và sử dụng tiền điện tử trong cuộc sống hàng ngày, chúng đã không nhận được ứng dụng hàng loạt cả trong kinh doanh và ở cấp độ người tiêu dùng. Chúng tôi tin rằng nó được kết nối với các vấn đề sau:
Vấn đề số. 1: Tiền điện tử rất khó hiểu
Vấn đề số 2: Bất ổn và biến động
Vấn đề số 3: Thiếu quy định pháp lý và kỹ thuật
Vấn đề số 4: Không có cách nào để xuất tiền kỹ thuật số ra thế giới thực
Các tổ chức phát hành tư nhân phát hành tiền kỹ thuật số của họ cho các mục đích khác nhau thực hiện thông báo và đào tạo người dùng về thị trường tiền điện tử, giúp họ hiểu bản chất và cách sử dụng nó. Cơ sở hạ tầng cần thiết cho hoạt động hiệu quả đang phát triển với tốc độ phù hợp để giải quyết vấn đề đầu ra tiền điện tử cho thế giới thực. Tuy nhiên, để thực hiện một hoạt động mua hàng hoặc trao đổi điển hình và nhận được kết quả dưới dạng hàng hóa thực hoặc tiền mặt, người dùng cần sử dụng dịch vụ của một số công ty, mỗi công ty cần thêm thời gian để thực hiện giao dịch và chi phí cao dưới dạng hoa hồng. Tại giao điểm của hai nền kinh tế tiền điện tử và nền kinh tế cổ điển, vấn đề phát triển một giải pháp duy nhất đã trở nên cấp bách hơn bao giờ hết.
Sự biến động giá của bitcoin (BTC) và các loại tiền điện tử khác là một trong những rào cản lớn nhất đối với việc áp dụng rộng rãi. Không giống như tiền giấy (fiat), các loại tiền kỹ thuật số hiện đại không có Ngân hàng Trung ương thực hiện chính sách tiền tệ để duy trì sức mua ổn định, điều đó có nghĩa là những thay đổi về nhu cầu có thể gây ra biến động giá lớn. Nếu người dùng không thể chắc chắn rằng sức mua của tài khoản của họ sẽ vẫn ổn định, họ sẽ không bao giờ sử dụng tiền điện tử làm phương tiện trao đổi thay vì các tài sản thay thế có giá trị ổn định. Mặc dù thực tế là nhiều nghiên cứu đã tập trung vào các chủ đề kỹ thuật như thông lượng giao dịch và hợp đồng thông minh, nhưng so với chúng, hầu như không chú ý đến việc cải thiện sự ổn định giá cả và chúng tôi tin rằng vấn đề này là một trở ngại nghiêm trọng hơn nhiều đối với việc áp dụng hàng loạt tiền điện tử làm phương tiện trao đổi.
CENTUS được thiết kế để duy trì giá trị ổn định, cũng như tạo thu nhập cơ bản thường xuyên (chủ quyền) cho chủ sở hữu của nó và nó là phương tiện trao đổi có sẵn cho bất kỳ ai kết nối với Internet.
CENTUS là một loại tiền kỹ thuật số mà độ tin cậy của mã thông báo được bảo đảm bằng cách neo vào đồng đô la Mỹ, trong khi vẫn được phân cấp hoàn toàn. Giao thức CENTUS điều chỉnh thuật toán việc phát hành mã thông báo CENTUS để đáp ứng với những thay đổi tỷ giá hối đoái của CENTUS so với USD. Điều này cho phép thực hiện chính sách tiền tệ tương tự như chính sách của các ngân hàng trung ương trên toàn thế giới, ngoại trừ việc nó sử dụng thuật toán phi tập trung dựa trên các giao thức mà không cần sự can thiệp trực tiếp của con người.
CENTUS có thể trở thành một giải pháp khả thi cho vấn đề biến động tiền tệ trong việc sử dụng nó cho dịch vụ cho vay và tiền lương, hoặc các hợp đồng tài chính lớn khác.
Ngoài ra, sự khác biệt quan trọng nhất giữa CENTUS và các đồng tiền ổn định khác là chủ sở hữu của nó nhận được thu nhập cơ bản thường xuyên (chủ quyền), được trả hàng tuần (thứ Ba và thứ Sáu), trực tiếp vào ví của người tham gia.
CENTUS được thiết kế để giữ giá ổn định bằng cách điều chỉnh ưu đãi theo thuật toán.
Nhiệm vụ của CENTUS là tạo ra sự giàu có và phân phối lại nó cho những người đơn giản - các thành viên mạng lưới Centus Seigniorage.
Stable Cent (CENTUS) là một loại tiền kỹ thuật số ổn định thuật toán trên blockchain Stellar. Số lượng Xu ổn định đang lưu hành tăng hoặc giảm theo thuật toán được chỉ định, tùy thuộc vào nhu cầu trên thị trường.
100 CENTUS ≈ 1 USD
Bằng cách cho phép người tham gia mua và bán CENTUS, hợp đồng thông minh đóng vai trò là nhà tạo lập thị trường. Để mua CENTUS, người tham gia cần chuyển tiền đến địa chỉ hợp đồng thông minh, nơi chúng được lưu trữ dưới dạng dự trữ biến đổi. Mục đích chính của dự trữ CENTUS là cung cấp cho người tham gia cơ hội bán mã thông báo CENTUS của họ bất cứ lúc nào; hợp đồng mua CENTUS bằng tiền từ dự trữ.
Hai lần một tuần, "hợp đồng thông minh" phát hành CENTUS mới và phân phối chúng theo tỷ lệ giữa các chủ sở hữu CENTUS hiện tại, có tính đến nhu cầu thị trường.
Do đó, chủ sở hữu CENTUS nhận được thu nhập gọi là "Seigniorage".
Chủ quyền là nguồn thu của nhà nước từ việc phát hành tiền. Các ngân hàng trung ương có thể ảnh hưởng đến mức độ chủ quyền mà các chính phủ nhận được bằng cách điều chỉnh tốc độ tăng trưởng của hệ thống tiền tệ.
Chúng tôi tin rằng việc phân phối CENTUS giữa các chủ sở hữu CENTUS hiện tại là cơ sở chính cho sự ổn định của hệ thống. Hơn nữa, chúng tôi chắc chắn rằng thành phần đầu cơ này đảm bảo sự ổn định của CENTUS.
Khi chủ quyền được phân phối giữa các chủ sở hữu CENTUS, đồng xu có hai nguồn giá trị: chính đồng xu ổn định CENTUS và chủ quyền mà mọi người nhận được hai lần một tuần. CENTUS Stable Cent được chốt với 1 US CENT (¢). Vì chủ sở hữu CENTUS thường xuyên nhận được chủ quyền, chi phí của CENTUS bằng 1 ¢ + chủ quyền.
Chúng tôi tin rằng nếu những người tham gia thị trường mong đợi các khoản thanh toán mới cho chủ sở hữu CENTUS trong tương lai gần, họ sẽ mua CENTUS vì lý do đầu cơ. Thuật toán CENTUS sẽ đáp ứng nhu cầu gia tăng này bằng cách tạo ra CENTUS mới để khôi phục giá coin xuống 1 US CENT.
Mặc dù nó có thể sẽ khuyến khích các nhà đầu cơ mua nhiều CENTUS hơn nữa để kiếm lợi nhuận từ những đồng tiền mới này và gây ra thời gian dài tăng nhân tạo và giữ giá trên 1 xu, thuật toán giảm chủ quyền trong khi tăng giá trên CENTUS sẽ có tác dụng có lợi trong việc ổn định tỷ giá hối đoái ở mức xấp xỉ 1 cent.
Thật tự nhiên khi nghĩ rằng việc phân phối tiền mới cho chủ sở hữu CENTUS hiện tại sẽ chỉ làm tăng giá trị của CENTUS, vì nó tạo ra một thành phần đầu cơ hấp dẫn thưởng cho mọi người chấp nhận CENTUS.
Chúng tôi tin rằng việc thêm thành phần đầu cơ này sẽ kích thích nhu cầu liên tục và chủ quyền lãi suất thả nổi sẽ chỉ thêm vào tiện ích của CENTUS mà không ảnh hưởng đến giá trị ổn định của nó.
Theo dự báo của chúng tôi, điều này sẽ làm tăng đáng kể giá trị thực và dài hạn của CENTUS cho những người tham gia thị trường.
CENTUS sẽ không được "in" cho tương lai - mỗi đơn vị sẽ được tạo khi người dùng mua nó và trong trường hợp trao đổi ngược - bị phá hủy. Do đó, tài sản được chuyển vào dự trữ đảm bảo cho cổ phiếu CENTUS.
Mã thông báo CENTUS, trước hết, không phải là mã thông báo để đầu cơ bởi các nhà giao dịch trao đổi, mà chủ yếu là một phương tiện tích lũy và tạo thu nhập của những người đơn giản – chủ sở hữu của nó, cũng như một phương tiện định cư giữa họ.
Chúng tôi không tìm kiếm nguồn tài chính bên ngoài từ các nhà đầu tư bên thứ ba, vì lý do trong tương lai họ sẽ yêu cầu lợi nhuận cao để đổi lấy các khoản đầu tư sớm, chúng tôi chân thành tin rằng những khoản lợi nhuận cao này có thể được gửi trực tiếp đến những người mua CENTUS mà không cần những trung gian đầu tiên này.
Giao thức CENTUS dễ hiểu hơn nếu bạn so sánh nó với Cục Dự trữ Liên bang (FED). Giống như FED, hợp đồng thông minh CENTUS kiểm soát mức giá và điều chỉnh cung tiền bằng cách thực hiện các hoạt động trên thị trường mở, trong trường hợp của chúng tôi bao gồm tạo mã thông báo CENTUS hoặc mã thông báo BILLEX (chúng tôi nói thêm về nó bên dưới). Như với FED, các hoạt động này được dự đoán bởi lý thuyết tiền số lượng để tạo ra mức giá dài hạn ở mức chốt mong muốn.
Thanh khoản CENTUS
Đồng tiền CENTUS bao gồm một cơ chế thanh khoản được thiết kế để giảm thiểu tác động của các lực lượng thị trường khi chúng gây ra sự biến động về giá trị của CENTUS. Hợp đồng thông minh CENTUS cung cấp việc bán vĩnh viễn các mã thông báo CENTUS mới với mức giá gần 0,01 đô la Mỹ. Và ngược lại, hợp đồng đề nghị mua lại và phá hủy mã thông báo CENTUS với mức giá gần 0,01 đô la. Hợp đồng thông minh cho phép chênh lệch trong đó những người tham gia đầu cơ có thể kiếm được lợi nhuận bằng cách duy trì chốt của đồng tiền.
Do đó, việc cung cấp mã thông báo CENTUS được xác định bởi nhu cầu: mã thông báo được phát hành hoặc rút khỏi lưu thông tùy thuộc vào thị trường. Ngoài ra, giá trị CENTUS nằm giữa giá mua và giá chào bán. Trong phạm vi được xác định bởi hợp đồng thông minh CENTUS, các giao dịch có thể được thực hiện trên thị trường thứ cấp mà không liên quan đến hợp đồng thông minh.
Doanh thu từ việc phát hành mã thông báo CENTUS mới được bảo lưu đầy đủ. Dự trữ được tạo ra chỉ thông qua việc bán mã thông báo CENTUS và mục đích duy nhất của nó là cung cấp cho hợp đồng thông minh CENTUS khả năng đổi mã thông báo, nếu cần. Chi phí duy trì dự trữ được chi trả bởi chính dự trữ.
Giới thiệu về Token
Đây là những token chính của hệ thống. Chúng được gắn với đồng đô la Mỹ và dự định được sử dụng làm phương tiện trao đổi và tạo doanh thu thông qua việc phân phối chủ quyền giữa các chủ sở hữu mã thông báo. Ưu đãi của họ tăng và giảm để duy trì mức giá neo ở mức 0,01 đô la Mỹ.
Quá trình thiết kế và phát triển CENTUS đòi hỏi kinh phí. Chúng tôi tin rằng quá trình này sẽ phản ánh các giá trị và nguyên tắc mà chúng tôi muốn thúc đẩy. Vì dự án của chúng tôi tuyên bố tính toàn vẹn và tính biến động thấp, chúng tôi không muốn bắt đầu phát triển CENTUS với đầu cơ công khai thông qua ICO. Theo đó, chúng tôi quyết định chỉ sử dụng những người sáng lập’ quỹ riêng là những người tham gia đầu tiên của dự án CENTUS.
Chúng tôi sử dụng một mã thông báo đặc biệt gọi là Debit Coin (DBC) để cung cấp bồi thường cho các thành viên sáng lập sớm và các bên quan tâm khác. DBC là một mã thông báo chứng từ có thể được chuyển đổi thành CENTUS theo ý muốn. Số lượng CENTUS nhận được trong quá trình chuyển đổi được mô hình hóa trước và phụ thuộc vào quy mô của nền kinh tế CENTUS: số tiền bắt đầu từ 0 và chỉ tăng nếu nền kinh tế CENTUS đạt được thành công thực sự. Điều này đảm bảo rằng lợi ích của chủ sở hữu DBC không xung đột với lợi ích của chủ sở hữu CENTUS.
Số lượng token DBC tương đương 100 triệu. Chủ sở hữu của các mã thông báo này có quyền bỏ phiếu về lãi suất chủ quyền được trả khi ưu đãi được tăng lên.
DBC có một hạn chế tích hợp đối với tác động của nền kinh tế CENTUS. Tỷ lệ chuyển đổi DBC sang CENTUS được giới hạn ở mức 1: 500, do đó tác động tích lũy của chủ sở hữu DBC bị hạn chế. Để giảm ảnh hưởng của bất kỳ thực thể riêng lẻ nào, quy mô cổ phần cũng được giới hạn tối đa 30% cho mỗi chủ sở hữu.
Chủ sở hữu DBC sẽ chỉ có thể nhận được chủ quyền đối với tài sản này trong trường hợp vốn hóa của CENTUS nhận được ít nhất 10 triệu. Sau đó, khi hệ thống phát triển và số lượng CENTUS đang lưu hành tăng lên, số lượng chủ quyền cho chủ sở hữu DBC sẽ tăng dần từ 10% lên 50% tổng số lượng chủ quyền tích lũy.
Do đó, chủ sở hữu DBC chịu rủi ro cao nhất. Điều này có thể được so sánh với việc nắm giữ cổ phiếu phổ thông của một công ty, trong khi CENTUS giống như một cổ phiếu ưu đãi, với chủ quyền "được đảm bảo", nhưng không có quyền biểu quyết và siêu cổ tức.
DBC luôn có thể được trao đổi cho CENTUS theo tỷ giá hối đoái hiện tại. Tỷ lệ DBC càng cao, bạn càng có thể nhận được nhiều CENTUS (giới hạn tối đa là 500 CENTUS). DBC chỉ có thể được trao đổi một lần, và chúng được loại bỏ khỏi lưu thông và đốt cháy trong quá trình trao đổi.
Giảm giá hối phiếu trên blockchain. Các mã thông báo này được bán thông qua đấu giá blockchain khi bạn cần giảm ưu đãi CENTUS. BILLEX không được gắn với bất cứ điều gì và mỗi hóa đơn hứa hẹn rằng chủ sở hữu sẽ nhận được chính xác một CENTUS tại một thời điểm nhất định trong tương lai trong một số điều kiện nhất định. Vì BILLEX mới được tạo ra được bán tại một cuộc đấu giá mở với giá dưới một CENTUS, bạn có thể mong đợi một phần thưởng cạnh tranh hoặc “sản xuất” để mua hóa đơn khi chúng được đổi ngang giá.
Các điều kiện theo đó BILLEX được đổi:
- Một hợp đồng thông minh tạo ra và phân phối CENTUS, có nghĩa là nó xác định sự cần thiết phải tăng nguồn cung CENTUS.
- BILLEX chưa hết hạn, i. nó được tạo ra cách đây chưa đầy 1 năm.
- Tất cả các token BILLEX trước đó được tạo trước khi các token BILLEX này được đổi hoặc hết hạn.
Kết nối các token để đảm bảo tính ổn định
CENTUS cung cấp sự ổn định giá cả bằng cách sử dụng các nguyên tắc kinh tế tương tự mà các ngân hàng trung ương trên thế giới dựa vào. Điều quan trọng nhất trong số này là Lý thuyết số lượng tiền. Trong phần này, chúng tôi sẽ đề cập đến các chủ đề sau:
- Làm thế nào để lý thuyết số lượng tiền liên quan đến mức giá dài hạn với cung và cầu tiền?
- Làm thế nào để Giao thức CENTUS đánh giá những thay đổi về nhu cầu bằng cách theo dõi tỷ giá hối đoái giữa CENTUS và các tài sản được chốt của nó?
- Làm thế nào để Giao thức CENTUS tăng và giảm việc phát hành mã thông báo CENTUS dựa trên tỷ giá hối đoái?
- Tạo thị trường để tăng và giảm nguồn cung CENTUS.
Lịch sử cho thấy rằng trong thời kỳ thị trường tăng và giảm, mọi người thường đưa ra quyết định có ý nghĩa kinh tế dưới ảnh hưởng của sự hoảng loạn và không quan tâm đến lẽ thường. Trong thời kỳ bùng nổ kinh tế, mọi người có nhiều tiền hơn, vì vậy họ muốn mua nhiều hàng hóa hơn, dẫn đến giá hàng hóa cao hơn, điều này khuyến khích nhu cầu về mức lương cao hơn, có nghĩa là mọi người thậm chí còn có nhiều tiền hơn. Hiện tượng này được gọi là vòng xoáy lạm phát, và đây là những gì đã xảy ra ở Đức vào những năm 20, Brazil vào những năm 80 và Argentina vào những năm 90. Tương tự, trong thời kỳ suy thoái kinh tế, người dân ngại mua hàng hóa, dẫn đến giá hàng hóa thấp hơn, khiến mọi người hoãn mua hàng cho đến khi giá giảm hơn nữa, v.v. Hiện tượng này được gọi là xoắn ốc giảm phát – Và nó gần như đã xảy ra trong cuộc suy thoái toàn cầu năm 2008. Trong những tình huống như vậy, một Ngân hàng Trung ương có trách nhiệm có thể bước vào để cắt đứt các vòng phản hồi phá hoại này. Vậy chính xác thì các ngân hàng trung ương đang đối phó với nhiệm vụ này như thế nào?
Hãy tưởng tượng rằng giá cả trong nền kinh tế nhà nước ở một mức độ nào đó, ví dụ, chi phí trung bình của một "giỏ hàng hóa" được xác định trước là 100 đô la. Lý thuyết số lượng tiền nói rằng nếu bạn tăng gấp đôi số tiền mà mọi người có trong tài khoản ngân hàng của họ, cùng một giỏ hàng hóa sẽ có giá trị 200 đô la. Tại sao vậy? Mặc dù số tiền danh nghĩa đã tăng gấp đôi cho tất cả mọi người, giá trị thực của hàng hóa vẫn giữ nguyên. Điều này có nghĩa là mọi người phải sẵn sàng chia tay với số tiền danh nghĩa gấp đôi để có được cùng một giá trị. Nguyên tắc tương tự cũng áp dụng theo hướng ngược lại: nếu chúng ta lấy một nửa số tiền tiết kiệm của mọi người ra khỏi nền kinh tế, cùng một giỏ hàng hóa sẽ chỉ có giá 50 đô la.
Mở rộng khái niệm này, chúng tôi sẽ xem xét trường hợp khi một ngân hàng trung ương cố gắng làm dịu lạm phát. Giá cao, liên tục tăng, có nghĩa là mọi người quá sẵn sàng chi tiền. Những gì chúng ta có thể làm là hạn chế số tiền mọi người phải khôi phục giá cả. (Chúng tôi không tập trung vào việc làm thế nào điều này có thể được thực hiện ngay bây giờ) Tương tự, điều ngược lại áp dụng cho giảm phát, khiến mọi người không muốn tiêu tiền. Để khôi phục giá cả, chúng ta có thể cung cấp cho mọi người nhiều tiền hơn. Ý tưởng đơn giản nhưng quan trọng này chính xác là những gì các ngân hàng trung ương làm để ổn định giá cả. Ngoài thực tế là các công cụ được sử dụng bởi các ngân hàng trung ương để thực hiện chính sách tiền tệ có thể phức tạp và khó hiểu, ví dụ, Hoạt động thị trường mở và Yêu cầu dự trữ, một ngân hàng trung ương thực hiện hai việc:
- Tăng cung tiền. Nếu một ngân hàng trung ương phát hiện ra rằng giá đang giảm, nó có thể tăng cung tiền để đưa giá trở lại mức trước đó.
- Giảm cung tiền. Nếu một ngân hàng trung ương phát hiện giá tăng, nó có thể làm giảm nguồn cung tiền để đưa giá trở lại mức trước đó.
Tăng và giảm cung tiền hoạt động vì lý thuyết số lượng tiền nói rằng giá dài hạn trong nền kinh tế tỷ lệ thuận với tổng cung tiền trong lưu thông. Sau đây là một ví dụ về lý thuyết được sử dụng để duy trì mức giá ổn định bằng một loại tiền tệ như CENTUS:
Giả sử bạn muốn liên kết một loại tiền tệ như CENTUS với đồng đô la để một mã thông báo luôn được giao dịch với giá 0,01 đô la Mỹ. Chúng tôi sẽ chỉ ra rằng bạn có thể làm điều này bằng cách tăng hoặc giảm nguồn cung cấp mã thông báo của mình tùy thuộc vào khoảng cách tỷ giá hối đoái hiện tại so với chốt mong muốn.
Đầu tiên, chúng tôi giới thiệu khái niệm tổng cầu. Về mặt khái niệm, tổng cầu mô tả có bao nhiêu người cùng muốn một đồng xu:
nhu cầu = (giá coin) * (số lượng coin đang lưu hành)
Điều này còn được gọi là vốn hóa thị trường của một đồng tiền, vì vốn hóa thị trường mô tả tương đương có bao nhiêu người đã chấp nhận chung một đồng tiền.
Hãy để X đại diện cho số lượng tiền xu đang lưu hành, tức là nguồn cung tiền xu. Giả sử rằng nhu cầu đã tăng lên trong vài tháng qua, vì vậy các đồng tiền hiện đang giao dịch với giá 1,10 đô la:
nhu cầu = 1,10 USD * X
Để xác định cách điều chỉnh nguồn cung tiền xu để khôi phục mức neo 1 đô la, chúng ta hãy giả sử rằng nhu cầu không đổi và để Y đại diện cho số lượng tiền xu mong muốn đang lưu hành:
nhu cầu trước = 1,10 USD * X
nhu cầu sau = 1,00 USD * Y
nhu cầu trước = nhu cầu sau
Giải pháp cho Y ngụ ý rằng để giao dịch một CENTUS lấy 0,01 đô la Mỹ, bạn cần tăng ưu đãi tiền của mình lên 1,1 lần:
Y = X * 1,1
As a rough estimate, the quantity theory of money finds that if CENTUS trades at some P price that is too high or too low, the protocol can restore long-term prices to $1 by multiplying the existing supply by P. There are some technical details, later we will talk about how fast the protocol should react, how fast prices will react, etc., but the main idea is that to maintain the peg in the long term, we just need to measure the price of CENTUS and adjust the token supply accordingly.
We have found out that CENTUS will maintain its peg in the long term if the token supply is adjusted when the token price has changed. How does the CENTUS pro- tocol measure the price of a token? How does this regulate the offer?
Here we handle these issues by providing the full CENTUS protocol specification. For a better understanding, we can assume that the protocol has all the technical properties of a traditional cryptocurrency, such as bitcoin (BTC), and the following additional features:
• The protocol defines the target asset for stabilization. This is a US cent for CENTUS. Then the protocol determines the CENTUS target rate to the target asset – 0.01 US Dollar for one CENTUS.
• The smart contract monitors exchange rates to measure the price. The smart contract receives the CENTUS-USD exchange rate source via the Oracle system. This can be done in a decentralized way, as we will describe later.
• The smart contract increases or reduces the supply of CENTUS tokens in re- sponse to deviations of an exchange rate from the peg.
• Smart contract distributes seigniorage to all existing CENTUS owners dur- ing periods of increased supply.
” If CENTUS trades for more than $ 0.01, the smart contract creates and dis- tributes new CENTUS via seigniorage. These CENTUS are determined by the pro- tocol set priority for owners of BILLEX tokens and DBC tokens.
” If CENTUS trades for less than $ 0.01, the smart contract creates and sells BILLEX tokens at an open auction to withdraw the coins from circulation. BILLEX tokens are worth less than one CENTUS, and they can be redeemed for exactly one CENTUS when the Stable Cents are created to increase the offer. This encourages CENTUS owners to participate in the sale of BILLEX and thereby re- duce the CENTUS supply in exchange for the potential payment of BILLEX to- kens in the future.
First, we will explain how the CENTUS protocol gets the CENTUS-USD ex- change rate. Since this information is external to the smart contract, the CENTUS protocol must implement so-called Oracle system, that is, a system that uploads external information to the blockchain. This can be implemented in several ways:
Secure channel. The simplest approach involves using a single channel that loads the real exchange rate into the blockchain, say from Coinbase, Krak- en, or another major exchange. It is obvious that this is the point of central- ization, but it is the simplest and most convenient option.
Delegated decentralized channel. The semi-decentralized approach is to select a small group of channel loaders by CENTUS owners voting. Using this set of channel loaders, the system can select the average exchange rate from them at fixed intervals. If it is discovered that an unscrupulous player is constantly trying to discredit the channel, he will be excluded from the system by coin owners who have an incentive to preserve the long-term value of the system. This reflects most of the advantages of decentraliza- tion. A similar scheme called Delegated proof of stake (DPoS) is even used in other protocols to generate entire blocks.
Decentralized scheme of Shelling points. A fully decentralized approach is to use the Shelling points scheme to determine the exchange rate. The scheme of Shelling points works like this:
- Anyone on the network can vote for what, as he/she think, was the average ex- change rate for the last 5 minutes.
- Votes are aggregated every 5 minutes and weighted according to the number of coins each voter possesses. In other words, the more coins you have, the more weight your vote gets.
- The weighted median value is taken as the true exchange rate. In addition, weighted 25th and 75th percentiles of price estimates are calculated.” People who guess from 25 to 75 percentiles are rewarded with a set number of newly created CENTUS. This award encourages people to vote, and even more so – to vote with consensus.
- At the request of the community, people who fall outside the 25th or 75th per- centile can be fined by reducing their number of votes.
Due to the fact that the calculation is based on the median, taking into account the number of coins in the voting pool, and a consensus-based reward mechanism is used, the scheme in a substantial way protects itself from unscrupulous participants if none of them owns more than 50% of the voting base of coins. Rules for rewards and punishments need to be developed to encourage enough people to vote. If these incentives are designed correctly, the result provides the same level of securi- ty as Bitcoin (which is also vulnerable if a single miner requires more than 50% CPU mining), Ethereum (if it implements proof of participation), and so on.
The secure channel and delegated decentralized channel approaches are simple ways to load the protocol safely, which represent a compromise between complete decentralization and ease of use. Schelling points scheme is newer, but we believe that we will be able to make it reliable by developing right incentives. In any case, all of these implementations are valid alternatives for uploading CENTUS USD prices to the CENTUS protocol.
Currently, CENTUS loads real exchange rates into the blockchain using Coinbase, Kraken, and Binance exchanges. It will be possible to consider a decentralized scheme of Shelling points in the future, when expanding the network.
Increasing the supply works like it is described below.
The basic option of increasing supply is implemented through continuous sales of CENTUS and accrual of seigniorage to token owners 2 times a week on Tuesdays and Fridays. The interest rate is determined based on the results of voting of DBC owners.
Let us consider the option of increasing the supply via BILLEX.
First, the smart contract counts all outstanding BILLEX tokens and orders them by creation time, starting with the oldest ones. This ordered sequence of bonds is called the BILLEX Queue.
Then the smart contract counts all issued CENTUS tokens, creates N new CEN- TUS tokens and distributes them as follows:
- BILLEX owners are paid first in order of priority (FIFO-first in, first out). If there are unpaid BILLEX tokens, the smart contract starts converting BILLEX to CENTUS tokens, one to one, according to their place in the BILLEX Queue. For example, if we need to create 100 CENTUS, we convert the 100 oldest out- standing BILLEX into 100 new CENTUS tokens. The FIFO queue encourages people to buy BILLEX sooner rather than later, since BILLEX purchased earlier is paid out before BILLEX purchased later.
After paying off all BILLEX, the system starts distributing seigniorage again to all CENTUS owners automatically.- Seigniorage are accrued to DBC owners after BILLEX repayment and after distributing payments to all CENTUS owners. In this case, the system dis- tributes seigniorage (the remaining new coins) proportionally to the DBC owners. For example, if we need to create 1 million CENTUS and there are 0 issued (out- standing) BILLEX and 1 million DBC in circulation, then DBC owners will re- ceive between 10% and 50% of coins depending on CENTUS capitalization. The remaining coins are distributed among CENTUS owners.
To prevent situations in which new BILLEX at the end of the BILLEX Queue will not have value for speculators due to excessive queue length, we have provided a limit on the validity of the BILLEX. The more the BILLEX Queue grows, the longer it will take to pay for new BILLEX at the end of the queue. This leads to a lower price for the new BILLEX, as speculators begin to demand higher returns for the extra time and risk they take. But if the price of new BILLEX drops to zero, the system can no longer reduce the offer – zero price means that no one wants to ex- change their CENTUS tokens for BILLEX tokens. To prevent this from happening, we forcibly terminate all BILLEX that have been in the BILLEX queue for more than 1 year, even if they have not yet been redeemed. We chose the validity period of BILLEX 1 year after the simulation showed that this has led to the creation of a reliable system with high prices for BILLEX even in conditions of very large price fluctuations. However, we reserve the details for further discussion of expiration dates up to 5 years in individual cases.
The mechanism for increasing the supply will be easier to understand in the fol- lowing example:
Let us say there are 500 BILLEX bills in the BILLEX Queue, 200 of which were created more than 1 year ago.
Let us suggest the system needs to create 1000 new CENTUS coins.
The system removes the 200 oldest BILLEX from circulation, leaving 300 BILLEX in the queue. If the system needed to create less than 300 coins, it would only buy back the oldest BILLEX. However, the system must create 1000 coins, so it buys back all 300 BILLEX.
The system needs to create another 700 CENTUS coins. The system distributes these 700 coins evenly to existing owners of 1000 CENTUS and 1000 DBC. Each CENTUS and DBC gets 700/1000 = 0.7 / 2=3.5 coins. For example, if you have 100 CENTUS or 100 DBC, you will get 35 coins in the process of increasing the offer and then sell them for USD. (Subject to CENTUS capitalization at $10 mil- lion)
Supply reduction works as follows. To destroy CENTUS, we must have an effec- tive mechanism that will encourage CENTUS owners not to use their CENTUS in exchange for future payments. We do this by creating a smart contract for BILLEX tokens and then selling them to CENTUS owners. As discussed earlier, BILLEX tokens are sold at an open auction at prices usually less than 1 CENTUS. In return, they promise a future payment of one CENTUS during periods of in- creased supply if the old BILLEX is not in circulation, if the BILLEX has not ex- pired and the BILLEX has not been redeemed within 1 year.
First, we will discuss the open bidding system. To sell BILLEX, the smart contract launches a continuous auction where bidders specify the bid and number of new BILLEX tokens. In other words, auction participants indicate how much they want to pay for each BILLEX and how many BILLEX tokens they want to buy at that price. For example, you can specify that they would like to buy 100 BILLEX at 0.9 CENTUS for one BILLEX. When the system decides to reduce the coin sup- ply, it selects orders with the highest bids and converts the owners’ coins to BILLEX until enough CENTUS are destroyed. As an example:
Let us suggest the system wants to sell 100 BILLEX.
Let us assume that there are three purchase orders in the bid stack: one bid for 80 BILLEX at 0.8 CENTUS each, one bid for 80 BILLEX at 0.6 CENTUS each, and one bid for 80 BILLEX at 0.4 CENTUS each.
The system calculates the clearing (settlement) price, which is the single price at which all offered BILLEX would be purchased. In this case, the clearing price will be 0.6 CENTUS.
The system executes winning bids at the clearing price: the first user will receive 80 BILLEX in exchange for 80 * 0.6 = 48 CENTUS, and the second user will re- ceive 20 BILLEX in exchange for 20 * 0.6 = 12 CENTUS.
The protocol places an artificial cap on BILLEX token price to ensure that it will not sacrifice the future too much to enter into contracts to issue coins in the present. We currently set this level at 0.10 CENTUS per BILLEX. We modelled the prices of BILLEX to show that even with a very wide range of demand models for CENTUS, this level is almost never reached.
QUAN TRỌNG: CENTUS issued on the Stellar blockchain are debited automati- cally from the addresses (accounts) of token holders using the Stellar Clawback function in case the rate deviates from the peg by more than 20%, followed by the accrual of BILLEX tokens in equal amounts.
Since the cost of producing paper money is low, the nominal value of a currency can be much higher than the cost of producing it. For example, it costs from 7 to 20 cents to print a US Federal reserve note depending on its face value. Conse- quently, the paper money printer makes a profit by creating more money. The value of money in comparison with its cost price is called seigniorage.
Seigniorage is the best tool for electronic money.
The largest number of seigniorages is associated with electronic money creation, since almost any amount of money can be created using electronics almost for free.
Similarly, CENTUS owners are entitled to receive an unconditional basic income from the seigniorage, which is a remuneration distributed among CENTUS own- ers.
We described earlier that the seigniorage is distributed twice a week – on Tuesdays and Fridays. The interest rate is determined by voting among participants – owners of CENTUS and DBC tokens.
According to the results of voting among participants on October 04, 2019, a deci- sion was made and recorded in the Telegram channel (https://t.me/coinger_im) to calculate votes based on two parameters:
- Medians of the seigniorage percent rates
- Majority of DBC votes
The values are calculated based on the average value of the two indicators.
At the same time, a mandatory condition for DBC token owners voting is the pres- ence of 100 DBC tokens or more on their wallet. This parameter can be changed up or down by DBC token owners’ decision.
More detailed calculation of the seigniorage percent rate Median value can be found in the description of the voting procedure: CENTUS Blog
As a result of monitoring the voting for the seigniorage rate among DBC owners held on 09.09.2019 and the analysis performed, it was decided to add the following to the current algorithm for calculating the seigniorage rate:
- Include the DBC asset ownership criterion in the calculation, considering 1 COIN = 1 VOTE. In other words, the more coins you have, the more weight your voice gains.
- After the votes are counted, award the BONUS in the minimum amount to those participants who vote only with one of the two voting assets. Subsequently, a transparent reward algorithm should be developed, possibly depending on the number of coins or based on a median prediction.
- Calculate the final seigniorage rate based on the rates that fall in the range be- tween the weighted 25th and 75th percentiles, based on the voting results.
- To reward people whose desired rates have fallen in the range from 25 to 75 per- centiles with a given amount of BONUS (perhaps the closer to the median, the higher the reward). The winners will receive an increased BONUS amount. This reward encourages people to vote and do it based on consensus.
- In order to prevent the undervaluation or overvaluation of economically justified seigniorage rates, people whose desired rates fall outside the 25 to 75 percentile range should not be rewarded with BONUS.
By weighing votes according to coin ownership, choosing an algorithm based on median calculation, and including a consensus-based reward mechanism, the scheme largely protects itself from unscrupulous participants, unless one of them owns more than 50% of the voting coin. This algorithm is excluded in the very principle of ownership of a DBC coin – no more than 30% for a single owner.
Implementation
The CENTUS monetary model is designed to support the CENTUS currency and provide confidence, especially when the currency market is still small. Its main functions include a reserve in USD stablecoins to maintain constant liquidity and reduce excessive volatility.
The CENTUS smart contract always offers to sell new CENTUS tokens or buy back and burn existing ones. This allows the market to determine the CENTUS supply while reducing volatility by limiting the price to within 0.01 USD peg.
Revenue from sale of CENTUS tokens is held in a reserve, the purpose of which is to ensure the value of CENTUS during the period when the currency acquires its independent trust. Funds in reserve is what allows the CENTUS smart contract to redeem CENTUS tokens when necessary. CENTUS reserves are stored only in USD stablecoins.
When more tokens are purchased from the CENTUS smart contract, the contract issues more coins; when tokens are sold back, they are redeemed from the reserve until the minimum level of 50% is reached, after which the BILLEX auction begins.
When the volume of CENTUS increases with the constant accrual of seigniorage, the total capitalization of CENTUS increases, although at the nominal price, the total value of tokens exceeds the CENTUS reserve. As a result, the CENTUS reserve does not contain the full market capitalization (cap) of CENTUS. In other words, the CENTUS reserve ratio is less than 100%.
The concept of a reserve ratio of less than 100% in the CENTUS context requires further clarification to avoid misunderstandings. For example, a reserve ratio of 95% does not mean that 95% of CENTUS issue revenue is deposited in the reserve, and the remaining 5% is withdrawn from the reserve for other use. Revenue is always fully deposited in the reserve; the decrease in the reserve ratio is due to the fact that the CENTUS contract awards seigniorage to token owners 2 times a week, increasing the supply of coins in the hands of owners. In other words, it is the CENTUS owners who benefit when our model reduces the reserve ratio – by increasing the number of their tokens.
Similarly, a 95% reserve ratio does not mean that the CENTUS contract will buy back only 95% of CENTUS tokens and become insolvent. Instead, the smart contract, when the reserve level reaches 50%, launches a discount auction of BILLEX and sells them to CENTUS owners in exchange for their tokens with a discount that is converted into profit when the bills are repaid later. Thus, the contract always has the ability to redeem any number of CENTUS tokens.
The CENTUS monetary model is primarily based on algorithms. All CENTUS project tokens are issued and circulated on the Stellar blockchain.
This transparently guarantees users that what they have been promised will actually be fulfilled. In the CENTUS model, our mechanism for providing liquidity, which allows participants to determine the CENTUS offer, is considered quite important, so it is implemented using the blockchain. We use a fully decentralized approach, so participants do not need to trust anyone to be sure that the code-based elements of our model are implemented exactly as described.
Not all components of the CENTUS model are based on computer code. Parts of CENTUS activities include interacting with the blockchain, such as managing reserves and awarding partner bonuses.
However, even when the implementation takes place outside of the blockchain, we strive to emulate the transparency of the blockchain as much as possible, informing CENTUS owners about such aspects.
In an ever-changing world, the CENTUS currency cannot rely on a static model. Code-based elements of our model may sometimes need to be modified. Other changes, such as working with new regulatory requirements, cannot be implement- ed through software algorithms. To keep up with the times successfully, the CEN- TUS currency must have a system for making decisions. It is also possible that we will use two blockchains, Stellar and Ethereum, in the work on smart contracts.
When the seigniorage is distributed among CENTUS owners, the number of tokens increases. As a result, the CENTUS reserve – the total net income from the sale of CENTUS tokens – contains less money than the market capitalization of CENTUS – the value of all CENTUS tokens in circulation.
The reserve ratio is defined as the percentage of the market value of CENTUS backed by CENTUS reserves. It reflects the level of market confidence in the CENTUS currency, regardless of the reserve.
For example, when people buy CENTUS knowing that the CENTUS reserve contains only 80% of the CENTUS market value, this is because they believe that CENTUS also has its own intrinsic value; otherwise, they sell CENTUS back to the CENTUS smart contract. Confidence in the independent value of CENTUS should be even higher if CENTUS are traded in the market when the reserve ratio is lower – say, 50%. In this case, the inherent value of CENTUS – its usefulness as a currency, its authority and recognition – is half its total value.
The reserve ratio also reflects the extent to which a CENTUS smart contract can affect the CENTUS price. When the reserve ratio is high, the CENTUS liquidity function has a great ability to mitigate price fluctuations. When the reserve ratio is lower, the CENTUS value is more determined and therefore depends on market confidence; the reserve plays a smaller role in stabilizing price movements.
The CENTUS reserve always remains solvent, even if the reserve ratio is less than 100%. When someone sells a CENTUS token back into a smart contract, the money that was put in reserve when the last token was issued goes to the seller.
The CENTUS monetary model is based on a variable reserve balance. It remains equal to 100% for the first 100 million tokens. At this stage, CENTUS is fully backed up. The CENTUS value is fixed and does not take into account changes in market confidence. Then, when more CENTUS are issued, the reserve ratio gradu- ally decreases, taking into account the increased confidence of the CENTUS market. The reserve ratio is slowly falling to a minimum of 10% when CENTUS market capitalization reaches US $ 1 billion.
Finally, after CENTUS capitalization reaches significant figures, it will no longer make sense to focus on the reserve in assessing the CENTUS value. The new stable system, which adjusts itself as necessary, will support the existence of CEN- TUS as an independent currency.
In this regard, our model simulates the evolution of other currencies: from fully backed by tangible assets (for example, the gold standard); to fractional reserves; based solely on the standard of its governing body.
The CENTUS reserve is stored only in USD stable coins, it shall not be invested anywhere, and serves only for the purchase of CENTUS via a smart contract or on the Stellar market (DEX). If the reserve account receives income from the demand/supply spread, this income used to support CENTUS shall be deposited in the CENTUS reserve.
Further development of CENTUS
Universal basic income (UBI) is a state or other institutional material support for community members. Universal (guaranteed) income consists in the absence of additional (along with belonging to the society) requirements for receiving assistance. It is believed that such a support system can reduce financial anxiety and improve mental and physical health, increase motivation to work. Typical arguments against a decrease in the desire to work and a corresponding decrease in productivity.
This is a social concept that involves regular payments of a certain amount of money to each member of the community by the state or other institution (such institution is represented by CENTUS seigniorage network in this document).
Universal basic (unconditional) income is regular payments, which are sufficient to cover basic expenses: rent, food, and clothing. They are provided regularly, free of charge, without any counter obligations, and do not depend on age, marital status or income level.
Initially, this method of interaction between the state and the individual was considered from the point of view of eliminating excessive social inequality. This was a key goal. And as an economic background, they used such a concept as “social dividends”. It was introduced by Clifford Douglas, British major, who was convinced that every citizen is entitled to a part of the national wealth.
Everything looks quite logical: if you are a citizen of the country, then you also own part of the national wealth. It is like being a shareowner and receiving a part of the company’s profit in the form of dividends.
Attempts to introduce cyclical payments of UBI in different countries are accompanied by discussions and contradictions of opponents and supporters of this measure of socio-economic support of the population.
Taking into account different approaches, states are trying to replace social payments with monthly accruals of UBI, thereby giving to the society the right to dispose its income based on its needs. However, it was calculated that, if Switzerland had introduced such kind of social benefits, the expenditure for the introduction of this measure would have been about 200 billion dollars per year. Given the financial condition and small population of this country, this figure is significant even for them.
So far, the main sources for payments of universal income have been named as follows:
- Universal basic income should replace all existing social benefits.
- Higher taxes. This is nothing new, and now all social programs are implemented by the state at the expense of taxes. Nevertheless, at present, social benefits and taxes are not symmetrical, that is, taxes are paid by some people, and benefits are received by others. The progressive tax rate is designed to redistribute money from the richest to the poorest.
We can often hear reproaches such as why those who work should support those who do not work, or who, in the opinion of society, do not work enough. What can we reply? It is in the interests of society as a whole. At least, this is how economists and sociologists explain this fact.
In addition, the redistribution of funds between social strata by other means is becoming more difficult.- Another source of payment of universal basic income are funds saved on reducing the bureaucracy. After all, officials dealing with social payments will no longer be needed. Every citizen will simply receive the amount due to him or her on a monthly basis.
- One of the options for obtaining funds for the payment of universal basic income is seigniorage (income received from the issue of money and assigned by the issuer on the property rights).
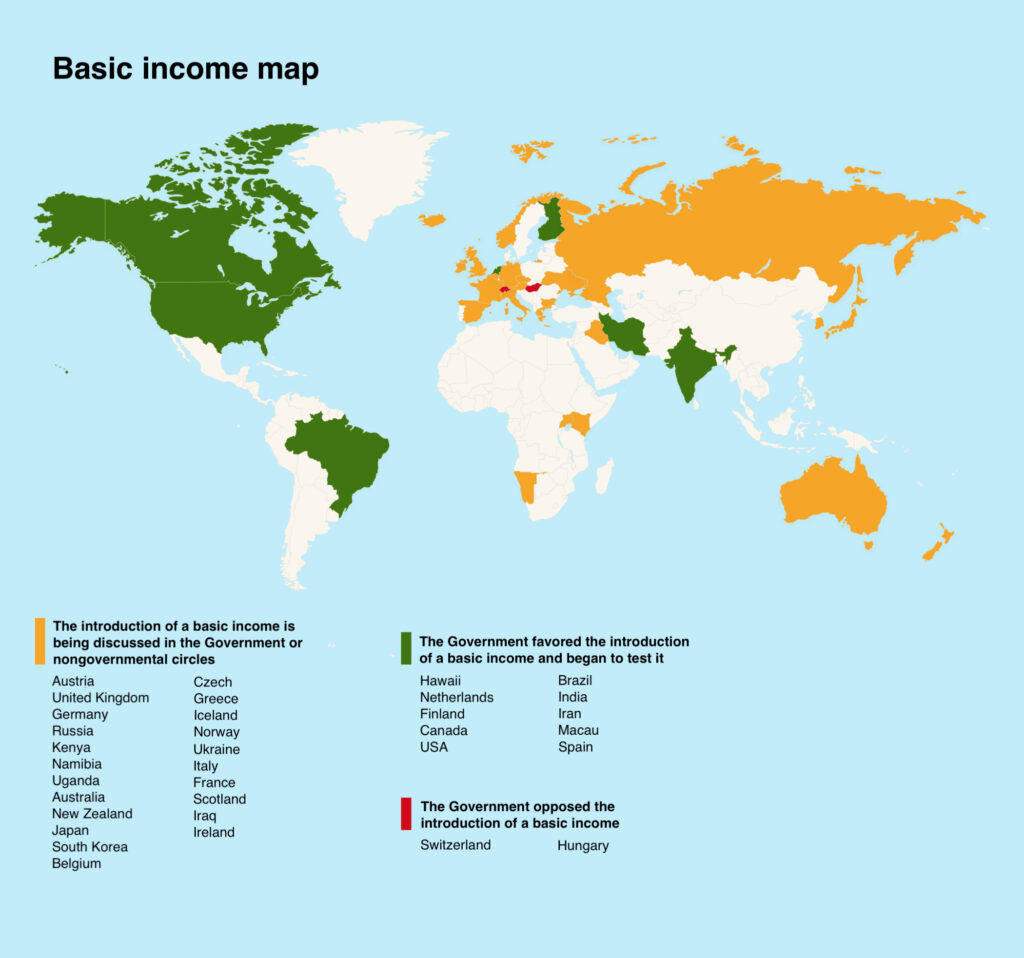
A number of countries have successfully implemented UBI accrual policy.
Canada
One of the very first experiments on the payment of a universal basic income took place back in the 70s in the city of Dauphin (Canada). The project is called Mincome. According to the project, each resident of the city received monthly payments for 5 years. We must admit that this was one of the longest experiments organized at the state expense.
Evelyn Forget, an economist at the University of Manitoba, studied the results of this experiment. She noted in her report that the level of employment has not decreased at all. At the same time, the number of volunteers has increased, and the social activity of the population has increased.
The rate of hospitalization in the city decreased by 8.5%. During the experiment, a larger number of teenagers graduated from schools, rather than leaving school study unfinished.
Namibia
A coalition of organizations launched a pilot project in Ochivero village, Namibia, with a population of about 1,000 people. For a year, each resident of the village had received 100 Namibian dollars per month. As a result, men stopped illegal hunting, children were not starving, and many children improved their school performance. Employment increased by 11% as people opened pastry shops, hair-dressing salons and brick-making workshops. Additionally, crime rates dropped by 42%.
India
In 2011, the Association of women entrepreneurs, supported by UNICEF, conducted an experiment that lasted a year and a half. Each adult in 10 villages was paid 200 rupees and a child was paid 100 rupees monthly. Economic activity has increased, and food and school attendance have improved. The government of India took into account the results of the experiment, replacing 29 different social programs with direct payments to citizens.
In addition, this year, Arvind Subramanian, an economic adviser to the government of India, suggested that the introduction of unconditional income at the national level should be considered. In the annual report for the government, the estimated amount was also named – 7620 rupees or $113 per year. Even such a small amount, according to many, could significantly reduce the level of poverty in the country.
Germany
In 2014, the German entrepreneur Michael Bohmeyer started implementation of the pilot programme “Mein Grundeinkommen” (my basic income). Several dozen randomly selected people had been receiving 1,000 euros each month for a year.
All participants of the project note that their sleep has become much calmer. However, not much has changed in their lives in general as students continued to study, workers continued to work.
The author of the project noted that the idea of basic payments is based on four principles: it is universal, it solves individual problems, it does not depend on any conditions and creates a high minimum standard of living for citizens.
Many countries are in the middle of an “experiment” now. We will be able to evaluate the results only after some time. You can find few examples of these countries below.
Finland
The Finnish national insurance authority has proposed replacing social benefits with a fixed payment for all adult citizens of the country, regardless of income level. It is expected to set payments at 550 euros per month, and later raise to 800 euros.
Kenya
In October 2016, Givedirect, the New York based charity organization which fights poverty in East Africa, launched the largest project thus far for paying an universal basic income in Kenya. Residents of 40 villages will receive about $ 22.5 per month for 12 years. This is not just a charity event, but a scientific experiment aimed at collecting and analysing data on the effectiveness of universal basic income.
USA
Participants of the Economic Security Project, launched at the end of 2016, are researching the potential benefits of universal basic income in developed economies. The initiators of the project with a budget of 10 million dollars are more than 100 organizations and individuals, including Chris Hughes, Facebook cofounder, and Sam Altman, Y Combinator Foundation President.
Spain
As part of measures to mitigate the social and economic consequences of the coronavirus pandemic, the Spanish government is going to introduce a universal basic income in the near future. Nadia Calvino, Minister of Economic Affairs, announced this on April 5, 2020. The Spanish government wants to maintain a universal basic income even after the epidemic. The Minister of Economic Affairs expressed hope that the universal basic income will remain a “permanent structural tool”.
There are about 20 ongoing experiments in the world related to the payment of universal income. Scientists are trying to figure out whether we are motivated enough to continue working without starving.
Any member of the CENTUS seigniorage network, a coin owner, is entitled to receive basic income in the form of interest accrued on the amount of coins in his wallet. The basic income rate is determined by network participants – owners of DBC tokens intended for project management. This is done to prevent CENTUS coin owners from indefinitely inflating the interest paid, thus no excessive supply of coins is created on the market.
In the CENTUS seigniorage network, not only participants who bought coins can receive basic income. It is also possible for those members of the community who do not have the opportunity to purchase tokens to receive such income. To do this, participants can promote the project at a certain stage by earning and accumulating special bonuses, which they can convert to CENTUS and receive basic income. Of course, they can sell these coins at any convenient moment.
In the future, as the project develops and the capitalization of CENTUS increases, in addition to interest charges, it is planned to add a payment of a minimum fixed amount in absolute terms, for example, from $50-100 to several hundred US dollars, to each CENTUS participant.
At the initial stage, we reserve the right to use any combination of seigniorage (basic income) payments, including dividing accruals depending on how CENTUS was received: for example, those who purchased tokens at their own expense can count on the maximum payout, while those who received them through bonus and other exchanges, as well as various incentive programs can receive accruals par- tially.
People living in developed countries take for granted the availability of a stable currency. If you are in the US with unlimited access to dollars or in the EU with access to euros, you may wonder why the world needs a digital currency with a stable price. However, in countries with weak financial institutions and unstable currencies, high rates of inflation and currency devaluation are common. We expect CENTUS with its stable price and integral seigniorage to be in high demand in these markets.
At the time of publication in the second quarter of 2020, annual inflation in Egypt was 6.8%, in Argentina – 50.3%, and in Nigeria – 12.2%. These are only those countries whose governments are relatively more stable. Let us look at Venezuela, which currently has an annual inflation rate of 9586%. What would you do if your savings were disappearing at a rate of 9586% a year? Faced with a rapidly depreciating local currency, people are looking for other ways to survive, often leaning towards the dollar. This effect is known as dollarization.
It usually takes three forms:
- First, the population may prefer to use the dollar instead of the local currency without any coordination from the local government. The US dollar is used as a de facto currency in a number of countries in Central Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa, and its adoption rate can be extremely high, despite the lack of official coordination. For example, for 2 years from 2006 to 2008, dollarization in the Seychelles jumped from 20% to 60%.
- Secondly, citizens of a country can demand the dollar, despite state capital controls that prevent the movement of the dollar across its borders. It is no secret that there was a black dollar market in Argentina, known as dollar blue, during the period of capital control from 2011 to 2015. Over those years, between $ 10 and $ 40 million per day changed hands at rates that were 25-30% higher than the official rate. These bets were even published daily in national newspapers, despite being officially illegal.
- Third, currency devaluation can become so severe that governments can officially switch to US dollars, as happened in Zimbabwe in 2009. Today the entire country requires regular deliveries of physical paper dollars and coins.
The prospects are obvious. Regardless of whether dollarization is officially approved, citizens, banks, and governments incur significant costs when importing physical US dollars. CENTUS, which allows millions of dollars to be transported by making the phone call and generates regular income, seems to be a significantly better alternative to paper dollars in all dollarization scenarios.
In conclusion: existing digital currencies have found an appeal in some countries with hyperinflation, for example, the use of bitcoins in Venezuela is growing as the country has faced a currency crisis. However, Bitcoin can never truly free people from their unstable local currency due to the lack of quote stability. For example, if bitcoin goes through a devaluation cycle, users do not see the difference between devaluing bitcoin and devaluing the local currency. Even if bitcoin only crashes once, people will want to switch to an alternative that is stable in price – if such option exists. Thus, the CENTUS seigniorage stablecent, which allows you to receive regular income, will be an excellent solution for developing countries experiencing rapid currency devaluation.
Today, many participants of the crypto market traders convert their cryptocurrency into stable coins pegged to the US dollar when there is turbulence in the cryptocurrency markets. To meet this need, a centralized solution, known as USD Tether, has been generated, but for reasons to be discussed later, a centralized solution such as Tether is unlikely to work in the long term, and as a result, Tether has faced significant negative sentiment. In addition, when the market falls and the trader keeps their assets in a regular stable coin, such as USD Tether, he does not get any profit, unlike CENTUS, which also has a stable price and at the same time brings income (seigniorage) to its owner.
A seigniorage digital currency with a stable price can meet the needs of digital traders. Therefore, cryptocurrency traders can naturally be enthusiastic about the new protocols, and here we expect initial demand for CENTUS Stable Cent.
CENTUS combines a digital currency that brings its owner a profit in the form of a seigniorage at the growth stage, and a stable coin pegged to the US dollar.
Due to instability, today’s cryptocurrencies are not suitable for even the most basic financial contracts that our economy relies on. Can you imagine a job for which you get one bitcoin per month, but you pay all your monthly bills in US dollars – what will happen to you and your family if the price of BTC falls? How about buying a home with a 30-year mortgage denominated in bitcoin, in a world where you probably still get paid in dollars? It is impossible to predict the development of events in such cases, because the credit and debt markets, and in fact the markets for any financial contract over time depend on price stability.
When entering a mortgage agreement, the greatest risk that you take as a lender is the risk of default. However, if this mortgage was denominated in an unstable asset such as Bitcoin, you are also exposed to a very high price risk. For example, the cost of a 30-year bitcoin-denominated mortgage may suddenly be very low if the price of Bitcoin falls by 90% on any given day over the next 30 years. To make deals, you must be prepared to either speculate on the price of Bitcoin for each loan you provide or find a specialist who will do this. In any case, the borrower will have to pay for your willingness to hedge price risks. This adds aspects, which are difficult to negotiate, to the simplest financial contracts.
A number of visionaries in the blockchain industry believe that we will soon see an ecosystem of “blockchain applications” that implement existing services with decentralized tools. For example, one day we may see “Uber blockchain” hoặc “Airbnb blockchain”, each using its own tokens. In fact, this is already happening with Filecoin, a service for decentralized file storage on the Internet.
Of course, if each blockchain application will create its own token, then there must be a conversion system between “a universal token that during its holding brings a constant income and has 100% liquidity” and the tokens of any of these applications. We assume that each person will become a owner of a universal token and will pay with it when using any blockchain application. Then, after payment, the universal token will be immediately converted into an app token at the market rate. This will be similar to your bank account in US dollars and using your debit card in another country, such as Spain, in which case your bank converts your US dollars to euros at the market rate every time you make a purchase, without having to think about it. At the same time, you also get a regular basic in- come in the form of a seigniorage for tokens.
If there were this ecosystem of blockchain applications that would require the use of a universal token, it would be very strange if this universal token were not stable in price with the condition of regularly received income. In other words, if you believe in the future of blockchain applications, you not only have to believe that a stable price coin will be required for exchange, but also hope that a stable price coin will be successful.
Annex
White Paper – documentation that describes the project, new process, or algorithm in detail. It is part of the company’s content strategy. Its purpose is to provide useful information about solving a particular problem.
Token, digital token – a term used in the cryptocurrency environment to refer to an intangible asset, a tool that gives access to certain services, or an internal currency.
Cryptocurrency – a type of digital currency, creation and control of which are based on cryptographic methods. As a rule, the record system of cryptocurrencies is decentralized. The functioning of these systems is based on blockchain technology. Transaction information is usually not encrypted and is available to public. Cryptographic elements are used to ensure that the transaction block chain database is unchanged (digital signature based on a public key system, sequential hashing).
Blockchain – a continuous sequential chain of blocks (a connected list) built according to certain rules that contain information (about transactions, agreements, and contracts). Copies of block chains are stored and processed independently on many different computers. Most often, the blockchain contains information about transactions in various cryptocurrencies, but blocks can also contain other information.
Decentralization – the process of distributing functions across the entire system without a single centre. A decentralized network (Peer-to-peer network) is a computer network based on the equality of participants. Often there are no dedicated servers in such a network, and each node (peer) is a client and in the same time function as a server. This organization allows you to maintain network performance with any number and any combination of available nodes.
Smart contract – program code that describes a set of conditions that cause certain events in computing systems to occur. It is designed for technical implementation of conclusion and maintenance of commercial contracts in the blockchain technology.
Thuộc về sao – an open source network for currencies and payments. The software operates in a decentralized open network and processes millions of transactions daily. Stellar relies on the blockchain for network synchronization.
Stellar address – a unique set of characters for sending / receiving cryptocurrency. Addresses are not repeated in the network. The address also acts as a public key that is used to sign blocks.
Fiat money – ordinary money, the nominal value of which is set and guaranteed by the state (dollars, euros, rubles).
The purpose of this White Paper is to provide information about the CENTUS project to potential buyers of CENTUS stable cent, DBC token, BILLEX token on the basis of which it will be possible to make a purchase decision. The information provided in this document is not exhaustive and does not imply any contractual obligations and can only be considered as marketing information about the project. The project information in this document is subject to change, update without prior notice and cannot be considered as a form of obligations of CENTUS, as well as related legal entities that support the project. CENTUS reserves the right to change the text of this document without any prior notice and at any convenient time.
Nothing in this document can be interpreted as an investment offer of any kind. This offer is not an offer to sell or buy securities in any jurisdiction. This document does not offer to purchase tokens to individuals and companies that do not have sufficient legal capacity to participate in a monetary exchange.
If you are not sure that you are eligible to participate in the CENTUS project, you should contact a professional legal, financial, tax or other consultant. Participation in the CENTUS project is voluntary.
What did inspire us to create CENTUS Stable Cent?
Basis is a project that also introduced the idea of increasing and reducing the supply of coins to maintain the rate peg. Basis was launched in 2017 and closed at the end of 2018, with $ 133 million in funds raised, an impressive list of advisors and a powerful team. The reason was that under US law, their tokens were considered securities and were subject to restrictions for securities.
We like lots of things about the Basis project, and this document relies heavily on their White Paper. We decided to take the best out of it but improved the scheme by adding a seigniorage payment to all CENTUS token owners, as well as a partial reserve to the smart contract, which acts as a market maker for participants, selling and buying CENTUS by using reserves.
We took into account the legal problems of Basis and offered BILLEX bills of exchange instead of bonds, which the participants themselves create through a smart contract in exchange for CENTUS. In this case, the legislative problem is completely solved, because any individual or legal entity can issue bills without the need to have a license, since the issue of bills is regulated by the Law of Great Britain on Bills (1882), which clearly specifies the procedure for their issue and circulation. CENTUS Protocol only offers participants a convenient platform for issuing BILLEX discount bills of exchange under their CENTUS. In addition, the CENTUS system with its partial reservation will allow increasing the supply without a mandatory 100% security, which will allow more flexibility in the policy of increasing the supply, especially at the first stages of development.
Imagine a world in which Bitcoin begins to compete with US dollars for the use of transactions. You are paid in bitcoins, but you pay for rent in dollars, or perhaps vice versa. This just does not make sense, given the inherent volatility of Bitcoin.
This article has presented CENTUS — a reliable, decentralized implementation of digital currency with a stable price and regular seigniorage for coin owners. We believe that if we can just make sure that the purchasing power of the currency does not change, people will give up the idea that it is not worth having a lot of digital currencies, and come to the understanding that storing their savings or incomes in CENTUS Stable Cent is reliable and profitable. We believe that this feature will help our tokens pass the acceptance cycle and help them move to the main exchange environment – a result that no other digital currencies has yet managed to achieve.
If you have any thoughts or would like to participate in the project, feel free to write to the authors listed on the title page. For the most up-to-date version of this document, visit the website http://www.centus.one